Q.Evaluate the Capitalist and the Socialist pattern of industrialization.
Approach
- Start the answer by briefly discussing capitalism and socialism.
- Discuss the factors leading to the evolution of the Capitalist and the Socialist patterns.
- Conclude Suitably.
Introduction
Capitalism is defined as an economic system in which the means of production, trade, and industry are owned and controlled by private individuals or corporations for profit. Also known as the free-market economy or laissez-faire economy.
Socialist Economy is defined as an economy in which the resources are owned, managed, and regulated by the State. The central idea of this kind of economy is that all the people have similar rights and, in this way, each and every person can reap the fruits of planned production.
Body
Capitalist Pattern of Industrialization
- Capitalism is the first stage in the history of the world to coincide with the phenomenon of industrialization in its full brown form together, the new economic institutions (like banking insurance) and the new technology that transformed the world.
- As a result of the renaissance in Europe in the seventeenth century, the methods of science, philosophy, and trade were being applied for utilitarian purposes.
- This led to the new discoveries of markets, and subsequently the industrial revolution (dominated by heavy machinery which repealed manpower) in European countries.
- The industrial revolution turned production by the masses to mass production.
- However, this capitalist mode of production resulted in inequalities between the classes and imperialism across the globe.
- This led to the development of the antithesis of capitalism by Karl Marx and Frederich Engels. However, socialism gets manifested after the Russian revolution in 1919 and the subsequent establishment of the USSR (now Russia).
|
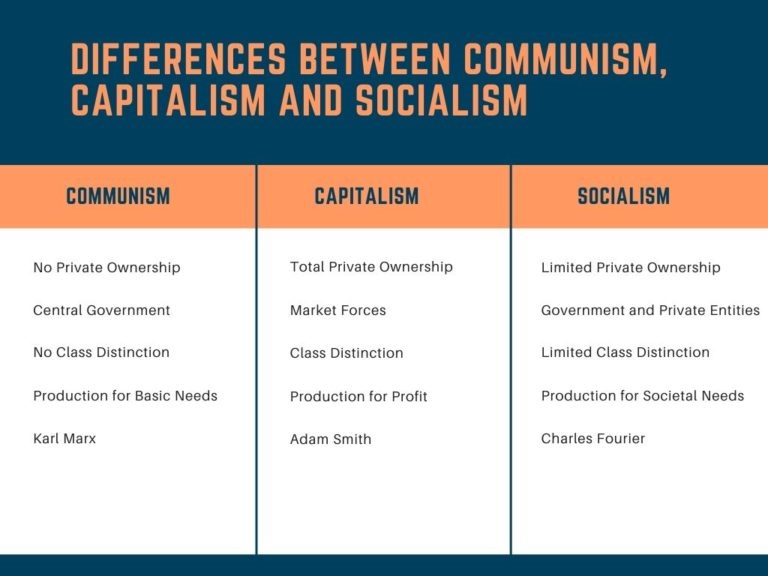
Differences between Capitalism, Socialism and Communism
|

Socialist Pattern of Industrialization.
- The Socialist pattern of industrialization emphasizes co-operative enterprise and various forms of community enterprise that would benefit the public as a whole.
- It implied activity to strengthen trade unions, friendly societies, and labour syndicates with or without the assistance of political parties.
- Nationalization was looked upon as a way of constituting an area of activity where the workers had no say.
- Governments evolved with state control of the economy. These governments used public welfare as their reference point.
- Hence the economy as it matured was called a planned economy.
- However, most socialists had an abiding fear of the state and state control as a possible source of intensification of exploitation rather than a solution to it.
Conclusion
Capitalism leads to the creation of wealth but it advocates distinction between the haves and have-nots. Socialism fills the gap between rich and poor, but at the same time it wipes out the encouragement to work hard, due to which the country's Gross Domestic Product falls down and everyone turns out to be poor. Thus, as every coin has two aspects, it is very difficult to say which system is better than the other.
