GS PAPER 1(2016)
In India, the Himalayas are prone to landslides, particularly n monsoon season, from months of June to October. Landslides are very common in the Himalayas especially during monsoon season. Himalayan landslides can be attributed to the fact that Himalayas lies at the convergence zone of two lithospheric plates, i.e., Indian plate in the south and Eurasian plate in the north. Thus geologically, it is considered very active as the height of the Himalayas is still increasing. It is made up of complex geology, geomorphology and geohydrology.
There are several big thrusts, viz., Main Boundary Thrust (MBT), Main Central Thrust (MCT), Almora Thrust, Vaikrita Thrust, Krol Nappe, Chail Nappe, etc., dividing Himalayas into number of fragments (Naithani et al., 1997). Presence of large number of faults and lineaments make the region geologically very fragile and susceptible to landslides at any scale (Mullik, 1996).
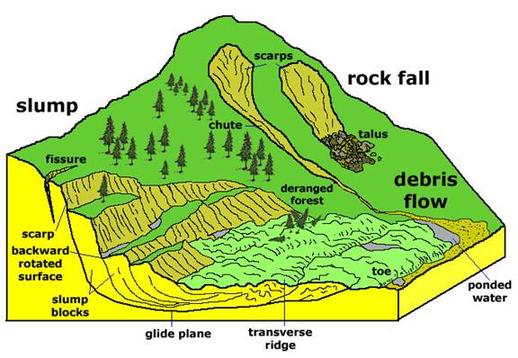
Little imbalance in elements of above-stated sheer stress factors might trigger landslides. During rainy season, additional water is added to the existing factors, which accelerate sheer stress factors. Thus, condition of the bedrock become fluid and landslides take place.
Natural Causes:-
(a) Earthquakes:- Himalayan regions are prone to frequent earthquakes leading to loosening of soils that further leads to landslides.
(b) Rainfall:- Himalayan region receives quite heavy rainfall that leads to soil erosion & landslides.
(c) Slope:- The steep slopes of Himalayan mountains is one of the major reasons of frequent landslides than any other mountain ranges in India.
Anthropogenic Causes:-
(a) Jhum Cultivation- popularly known as slice & burn type of cultivation practiced particularly in the Himalayan region.
(b) Chopping of trees- Himalayan region is centre of huge diversity when it comes to trees & this diversity has led to indiscriminate chopping of trees.
(c) Illegal mining & Industrial activities too have contributed a lot when it comes to reasons of landslides in the region.
Although Anthropogenic causes can be restricted, Natural causes are beyond human control but their impact can be minimised to lowest by the following steps:-
(a) Tree plantation.
(b) Building catchment areas to capture extra rainfall water.
(c) Stopping Jhum cultivation.
(d) Teaching people about landslides & ways to mitigate.
(e) Constructing a permanent assessment team comprising scientists & geologists that would look into the matter.
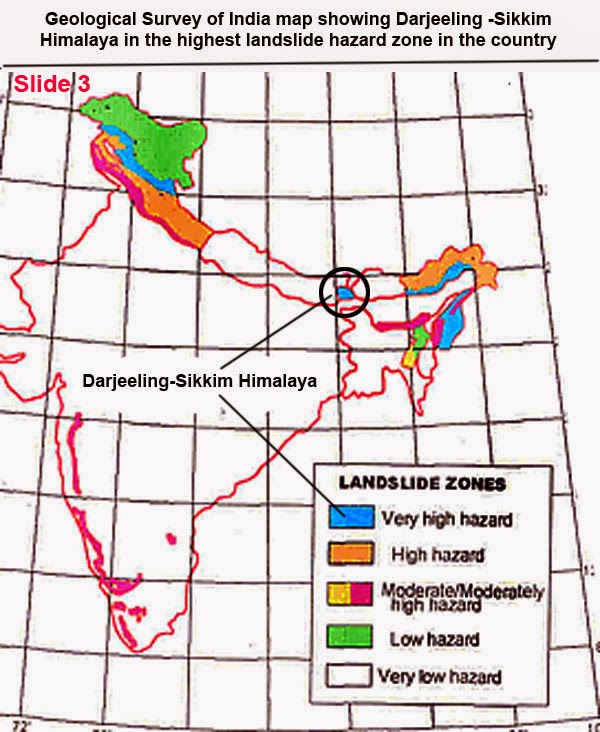
Suggestions:-
Better disaster management forces should be deployed.
Satellites should be deployed for prior alert info.